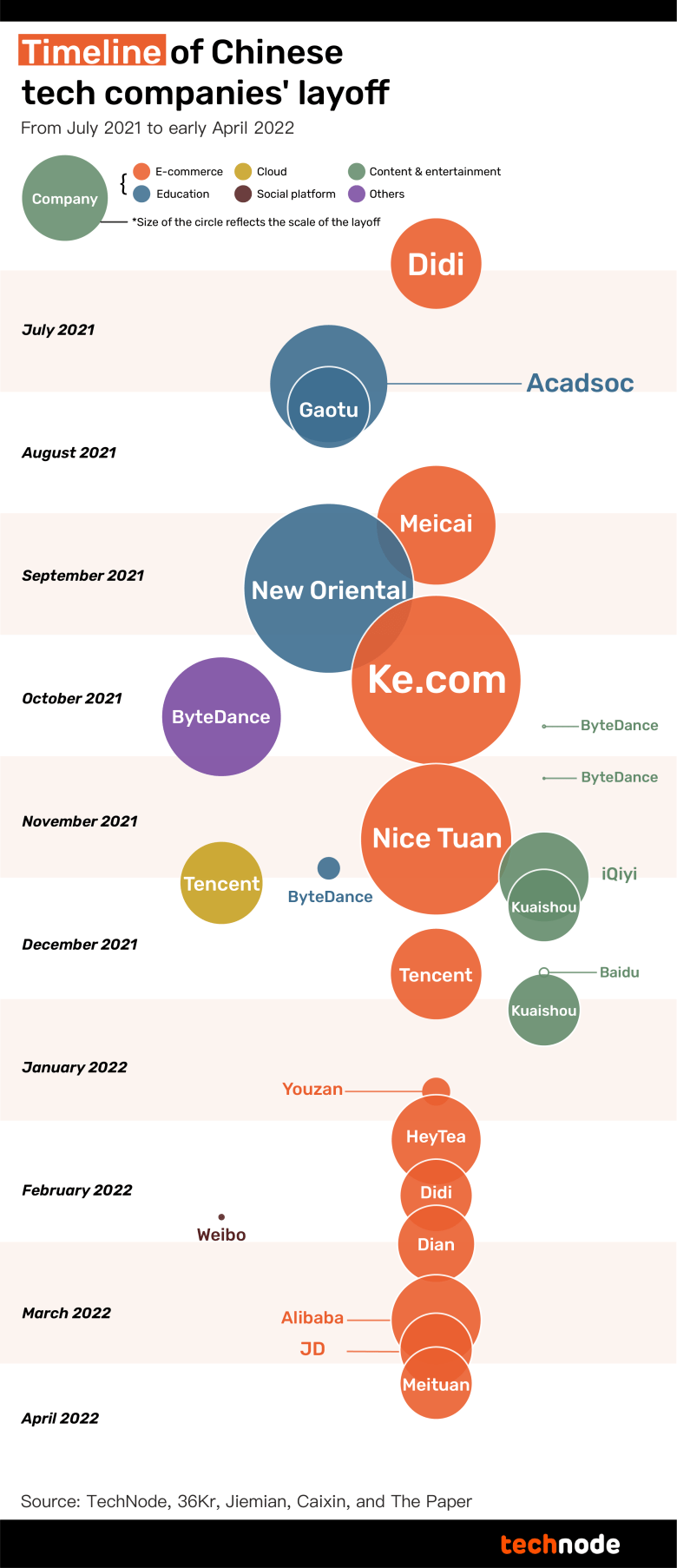
After China’s ride-hailing giant Didi was put under a cybersecurity review by the Chinese authorities last July, the country’s internet sector quickly entered a period of painful adjustments. Companies began closing unprofitable units and cutting staff wherever they could. Layoffs have since become so widespread that some Chinese tech majors have been attempting to soften the blow by telling fired employees that they have “graduated,” but it has become increasingly difficult to put a positive spin on such moves, as China’s consumer-facing tech companies go through a significant upheaval.
Since July 2021, major Chinese tech companies have laid off at least 72,779 employees, TechNode research has found. After compiling news reports, company statements, and other sources from the past nine months, TechNode found 27 instances where major Chinese tech companies were reported to be making significant layoffs, with at least 10 such instances affecting more than 30% of employees at their respective companies. Some firms dismissed entire departments almost overnight.
After combing through the statistics, it is clear that layoffs have become a regular occurrence at Chinese tech companies. In the past nine months, there has been an average of two rounds of layoffs per month. Moreover, in the same period, ByteDance has had five separate rounds of staff reductions alone, making it the top cutter among the major tech companies in the country.
China’s “great layoff” first hit the edtech sector, prompted by a surprise national regulation barring all private curriculum tutoring, which took effect in July. It then hit less profitable units in the e-commerce sector, and most recently, it spread to Meituan, Alibaba, and Tencent, powerful leaders of their own sectors that had previously proven largely immune to the effects of any regulatory changes or downturns.
Education, e-commerce, and the content and entertainment industry are the three sectors to bear the main brunt of this wave of layoffs. But just how far-reaching have the cuts been?
Cloud services, social platforms, and more
In March, Tencent, a major cloud service provider in China, started a 20% layoff of its team in the sector, affecting an estimated 12,000 employees. The firm’s Cloud & Smart Industries Business and Platform and Content Group took the biggest hit.
Twitter-like microblogging service Weibo, one of the biggest social platforms in China, laid off at least 200 employees and introduced a stricter performance review standard in February 2022. Weibo has declined to describe the moves as a layoff, saying they were “structural adjustments.”
ByteDance also cut numbers at its customer service unit in October 2021, removing somewhere between 30% and 70% of the team due to what it termed “business adjustments.”
Didi, which is still going through a national cybersecurity review that launched nine months ago and is looking to delist from the US stock market, reportedly cut 20% of its employees in February.
Content and entertainment
The content and entertainment industry is another area where players large and small have been handing their employees grim news. Since last July, four major companies in the sector have undergone six rounds of dismissals and restructuring.
ByteDance laid off at least 179 employees in two rounds last year, one of which was mainly focused on its gaming development business, Ohayoo. The company said that recently-hired college graduates would be reassigned to other vacancies as part of the round. The TikTok parent company followed this with another round of layoffs on October 20, aimed primarily at its commercialization and gaming businesses.
TikTok’s major rival in China, Kuaishou, started to lay off staff at the end of 2021, first in its commercialization team and then across multiple sectors. The company reportedly removed somewhere between 10% and 30% of its employees.
iQiyi, a Netflix-like streaming platform backed by Baidu, was reported to have cut between 20% and 40% of employees in December 2021. The company promised to compensate these unlucky employees, offering them bonuses based on how long they had worked at the firm.
While it’s undoubtedly been impacted by the overall economic downturn, the content and entertainment sector has also been hit by regulatory scrutiny, with crackdowns targeting celebrity culture and related idol content as well as the gaming sector. Pop Idol-like shows on platforms such as iQiyi have been banned and China put a pause on issuing new gaming licenses last year, essentially stopping companies from releasing new games. In addition, China has introduced strict controls targeting teenage players, limiting their playing time and payment for games. In response, Chinese gaming companies have shut down numerous development projects and turned to overseas markets, with their China workforces naturally being affected.
E-commerce
E-commerce, a longtime booming sector in China, has also seen contractions. From July 2021 to March of this year, at least 11 major tech companies in the industry have downsized their workforces, according to TechNode statistics.
Most recently, Meituan began on April 8 with an up to 20% cut across its business lines, including its core food delivery and hotel booking businesses.
Chinese e-commerce giant Alibaba has been through two rounds of layoffs in the first quarter of 2022 alone. The first round was in January this year, when it cut headcounts at its food delivery platform Ele.me and local shop review business Koubei. Two months later, Alibaba’s layoff expanded to the entire local service sector, with 30% of its employees losing their jobs.
Tencent also announced that it was making 30% of the staff at its e-commerce platform Mogujie redundant in late 2021, blaming the unit’s poor market performance.
Community group buy, a subsector that caught on during the height of the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic in 2020, has seen deep cuts as part of the ongoing layoffs. The cash-burning sector quickly cooled down after the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) demanded companies stop price dumping and other unfair competition practices in December 2020.
Smaller players in this subsector have been hit hard, with one example being Tongcheng Life, which filed for bankruptcy last July. Those backed by bigger companies have also been forced to make adjustments to remain competitive. Didi’s Chengxin Youxuan cut about a third of its staff, while Alibaba-backed Nice Tuan stopped operating in several cities.
Fast forward to late March, and JD was reportedly planning company-wide cuts of between 10% and 30%. Its community group buy unit Jingxi is thought to see the deepest cuts.
Other tech companies offering local services, such as apartment rental platform Ke.com and farm-to-table grocery startup Meicai, have followed suit. Ke.com cut its entire development team in October 2021, while Meicai laid off nearly half of its workforce around September 2021.
Dian, a Chinese startup offering rental charge packages for phones, was reported to have laid off 40% of its employees on March 1. According to Chinese financial media Lanjing, the company dismissed at least 2,000 employees. However, the company denied the news, saying it was merely making “adjustments in employee structure.”
In addition, popular milk tea brand HeyTea, which makes heavy use of e-commerce and online promotions to support its business, was reported to have cut its workforce by 30% in February this year.
Education
After China’s new regulation on education agencies took effect in July 2021, there were at least five rounds of layoffs in tech companies focusing on education. More than 5,400 people lost their jobs.
Companies in the sector saw their stock prices crash after July 24. Within a day, Gaotu fell by 54%, New Oriental by 63%, and TAL Education saw more than 70% wiped off its share price.
Gaotu was reported to have laid off more than 10,000 employees in early August 2021. Another education giant New Oriental reportedly dismissed over 40,000 employees in mid-September. It wasn’t just the leading names in the industry who were hit, however, Acadsoc, a Chinese company offering courses by foreign teachers, laid off 90% of its workforce on July 29, 2021.
Chinese tech unicorn ByteDance was also forced to make cuts. The company went through a series of downsizings in its education sector, with a first round in early August followed by a second round in December, shedding more than 1,000 employees.
Looking ahead
On April 8, China’s internet regulator, the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC), confirmed in a statement that 12 major Chinese tech companies (Tencent, Alibaba, Ant Group, ByteDance, Meituan, Pinduoduo, Kuaishou, Baidu, JD, NetEase, Weibo, and Bilibili) have laid off 216,800 staff from last July to March. However, CAC said “the number of employees in internet companies has remained stable,” disputing the layoff trend, adding that these companies have also hired about 295,900 new employees during the period.
As painful as these adjustments have been to date, it seems unlikely that Chinese tech majors are in the clear just yet. Regulatory scrutiny will continue (perhaps in a more predictable fashion as the government prioritizes economic growth), rising geopolitical concerns mean that firms listed on US exchanges, in particular, will come under pressure, and China’s ongoing attempts to pursue a ‘zero Covid’ policy may mean further disruption for businesses.
Since early March, China has extended lockdowns in the key growth city of Shanghai and introduced new control measures across the country to adhere to its zero Covid policy amid a resurgence in the number of coronavirus cases. As China’s economy takes a hit, the country’s tech sector is likely to come under more pressure. China’s State Council executive meeting on April 6 also acknowledged the challenge ahead, admitting that the country’s economy faces “complexity and uncertainties” that have exceeded expectations, and that “the recent Covid-19 outbreak in China has increased difficulties for market entities, and increased new downward pressure on the economy.”
There are some glimmers of hope, however. Although Didi’s investigation put a pause on Chinese tech companies seeking overseas listings, there appear to be moves to help Chinese businesses raise money more easily on foreign stock markets. Chinese Vice Premier Liu He said in a mid-March meeting that “China continues to support companies seeking to go public overseas,” offering the first major positive signal on the issue in nine months. Moreover, China’s securities regulator has proposed changes to long-standing rules in an attempt to avoid US-listed Chinese companies being delisted by American regulators.
Nevertheless, the big picture remains unpredictable for China’s tech powerhouses. After years of unbridled growth, it’s clear that the industry has been through a turbulent period of late. Whether the widespread “adjustments” made across multiple sectors will be enough to stave off further disruption remains to be seen.

